Karelian Isthmus: Geography and Climate
Geography:
The isthmus shows evidence of the ancient Weichsel glaciation: its long, winding morainic hills, which reach an elevation of about 205m (670 ft) in the south, are separated by countless lake-filled hollows (there are about 700 lakes on the isthmus) and swamps.
Karelian Landscape

Karelian Lake

The isthmus is mostly covered by coniferous forests formed by Scots pine and Norway spruce, with numerous small grass low moors and Sphagnum peat bogs. Forests cover more than three-fourths of its total area.
Karelian Forest

Swampy areas occupy on average 5.5% of the territory. In the large contiguous area along the shore of Lake Ladoga , in the southeastern part of the isthmus, bogs occur much more frequently than in other parts. The soil is predominantly podsol, which contains massive boulders, especially in the north and northwest, where large granite rocks occur.

Vuoksi (Vuoksa), the largest river, runs southeastwards from Lake Saimaa of Finland to Lake Ladoga, dividing the isthmus into two uneven parts. A western branch, which is now overgrown, was an alternative route for the Karelians to reach the Gulf of Finland when the River Neva was blocked by enemies. The Saimaa Canal bypasses the Vuoksi following this old outflow and enters the Gulf of Finland near the medieval city of Vyborg.
The entire run of the river is 162 kilometers (100 miles) via the Priozersk branch or 150km (94 miles) via the Taipale branch. For most of its length, the river broadens out to a series of lakes bound together by shorter river-like connections. One of these lakes, Suurselkä, close to Priozersk, was renamed to Lake Vuoksa.
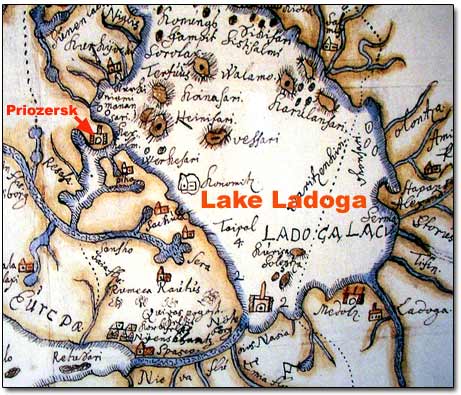
Lake Ladoga is the largest fresh water lake in Europe and it has been very involved in the history of the nation. 17 700 square kilometers in size, this impressive lake has approximately 660 islands. Most of these islands are situated on the northwestern coast. The well known historical Valaam islands are among them.
Lake Ladoga on Swedish Map of 1570
Lake Ladoga Shore

On the Beach

Climate:
The climate of the isthmus is moderately continental, with 650-800mm (25-32 inches) average precipitation per year, long snowy winters lasting from November through mid-April and occasionally reaching about -40°C (-40 F), moderately cool summers and short frost-free period. Compared to other parts of the Leningrad Oblast, the winter here is usually milder due to the moderating influence of the Gulf of Finland, but longer.